Defence in Depth
Layering security controls through your application
Lilly Ryan
What Is Defence in Depth?
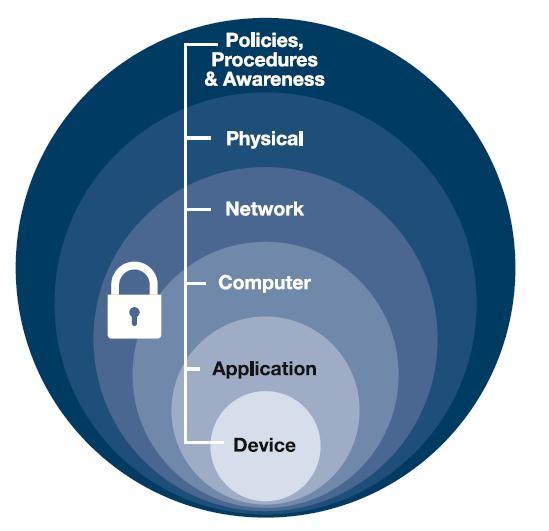
Defence/defense(*) in depth (sometimes referred to as "layered security") is an approach to securing a system, service, or piece of software that focuses on including strong security controls on all layers of a stack or design, rather that focusing all effort on securing only the outward- or user-facing parts of the solution. The aim of this practice is to build redundancies into security controls so that, if one control fails (either temporarily or permanently), the other controls will still be able to protect the application.
For example, a web application built with defence in depth principles in mind may have implemented a Web Application Firewall (WAF) as a first line of defence against malicious, user-submitted data, but will also have set strong security flags on application session cookies, implemented a strict Content Security Policy (CSP), and application logic that does not directly pass user-submitted strings as program variables. This requires the cooperation of the entire team involved in building the web application to ensure that security controls have been implemented correctly across the application and that those controls work together to prevent attempts to breach or maliciously manipulate the application.
* "Defense" is the US English spelling. "Defence" is the UK/AU English spelling.
Why Do Defence in Depth?
A team may practice defence in depth to ensure that the system or application is able to defend against attacks even in the event of the failure of the outermost layers of control.
In this way, an attacker is less likely to be able to thoroughly exploit or penetrate the system because the team that designed it has not assumed that the outer layer of defences will hold up against all types of attack, or that there is no way past those defences that they have not anticipated.
How to do Defence in Depth?
Defence in depth can be practiced at any stage of the software development lifecycle, but it is most effective when first considered during a threat modelling exercise at the start of an iteration, or during project kickoff. It involves assessing and implementing strong security controls to each element of the design.
Considerations may include (but are not in any way limited to):
- the "principle of least privilege" (ensuring all users or accounts have only the minimum permissions required to perform their functions, and no more)
- authentication controls (e.g. password policies, multi-factor authentication)
- network security controls (e.g. firewalls, security groups, ingress and egress rules)
- physical controls (who can access critical infrastructure)
- insider threats (not just assuming that the only threats to your application will come from attackers outside of your organisation)
- "assume breach" (assuming you have already been breached, and thinking about what internal controls are in place)
Look at Defence in Depth
Links we love
Check out these great links which can help you dive a little deeper into running the Defence in Depth practice with your team, customers or stakeholders.